Voice limit
Voices are used to play the waveform data referenced by Waveform Regions.
Depending on the settings of a Cue, multiple waveform regions can be played simultaneously.
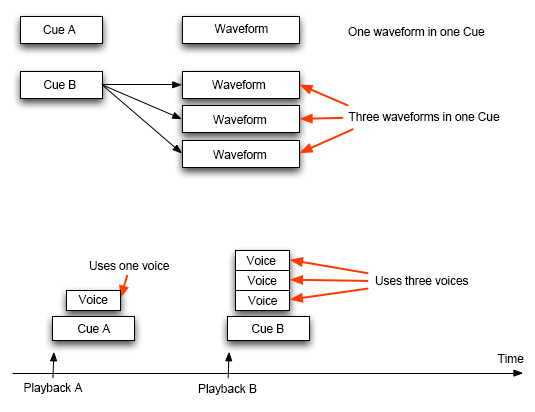
Voices are acquired a the voice pool
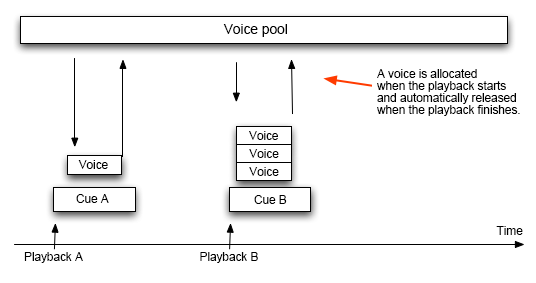
On the program side, Voice resources are secured from voice pools.
When a waveform needs to be played, voice resources are secured from a voice pool compatible with the codec used to encode the data.
These resources are returned to the pool when the playback is completed.
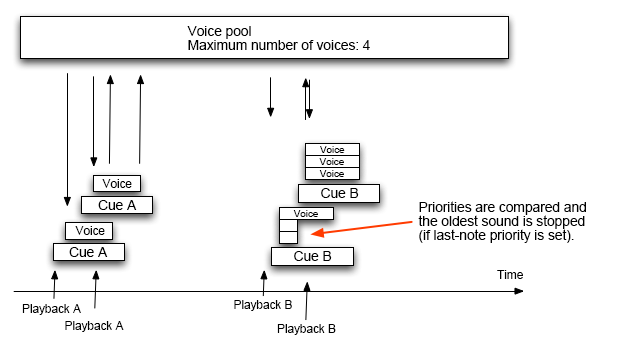
When the maximum number of voices has been reached, voice limiting is performed.
If new sounds are triggered while all the available voices are already in use, voice limiting will occur and a voice may be stolen to play the new sound.
The voice stealing process is based on the Voice Priority value: the oldest voice with the lowest priority is taken away.
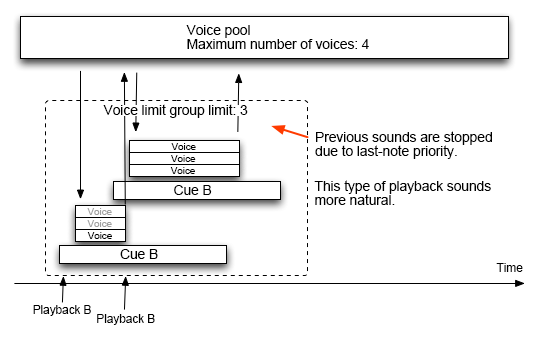
Voice Limit Group
The Voice Limit Group is a way to group voices for priority comparison.
When the new Voice is part of a Voice Limit Group, ADX first looks within that group for a voice to steal.
If no voice could be stolen, the other voices from the pool are examined.
Priority to the latest: when two sounds have the same priority, the sound triggered the most recently will be prioritary.