 |
CRI ADX
Last Updated: 2025-05-07 13:34 p
|
 |
CRI ADX
Last Updated: 2025-05-07 13:34 p
|
3D positioning expresses the position in space by specifying the x, y, z coordinates.
It automatically finds the direction and distance attenuation based on the positions of the sound source and the listener.
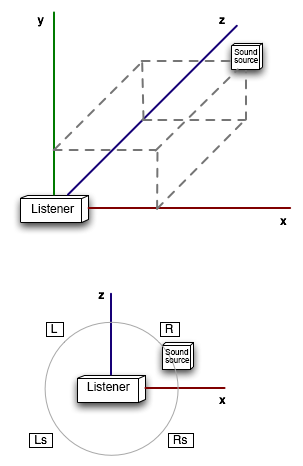
Although the calculations are performed automatically, the application is required to continuously (once every frame) update the positions of the source and the listener.
The 3D positioning-related parameters are the minimum and maximum attenuation distances, the Doppler coefficient, and the emission cone settings. These parameters are set in the Cues.
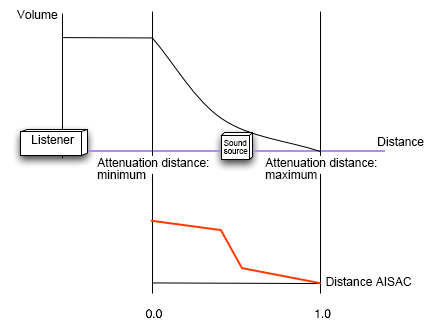
You can also use AISAC to design specific distance attenuation curves, and to change the sound according to angle variations.
For example, you can filter the sound when it is located in the back of the listener, or even switch to a totally different sound when the source is far.
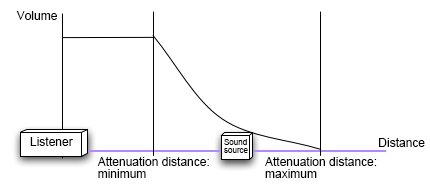
The distance attenuation AISAC is used to make parameter changes according to the attenuation distance (from the minimum to the maximum attenuation distances).
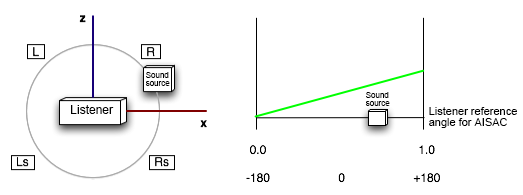
The listener reference azimuth angle AISAC is used to make parameter changes according to the sound source angle with respect to the listener.
For example, you can apply a filter effect when turning to the surround side.
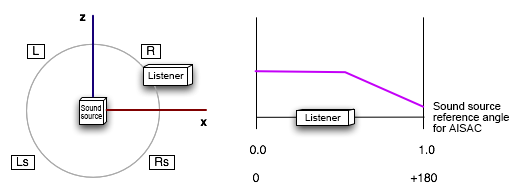
The sound source reference azimuth angle AISAC is used to make parameter changes according to the listener angle with respect to the sound source. For example, you can add a filter effect to the sound source cone.
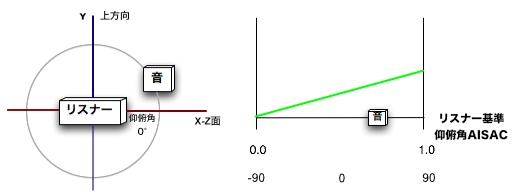
The listener reference angle of elevation AISAC is used to make parameter changes according to the sound source angle of elevation with respect to the listener.
For example, you can add a filter effect when the sound source rotates upward.
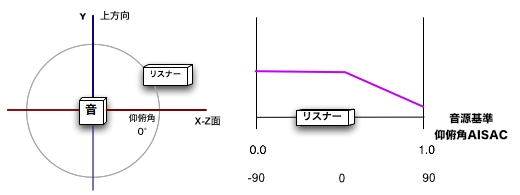
The sound source reference angle of elevation AISAC is used to make parameter changes according to the listener angle of elevation with respect to the sound source. For example, you can add a filter effect to the sound source cone.
There are some 3D positioning features that can only used from the program side.
For example, if you use the focus function, you can handle the position of the microphone separately from the position of the distance and angle sensors, etc.