 |
CRI ADX
Last Updated: 2025-05-07 13:34 p
|
 |
CRI ADX
Last Updated: 2025-05-07 13:34 p
|
Sounds can be grouped in different ways.
For example:
It is useful to use Categories in ADX to implement these groups.
You can limit the number of Voices using the Cue limit of the Category.
You can roughly prioritize the Category by adding an AISAC, configuring the Voice priority and enabling the AISAC initial value.
You may want to divide the Categories for a more granular control of groups.
You can create Category Groups and assign multiple Categories to a single Cue.
Categories create rules which can affect an entire game.
You can create a rule so that the limits should not be exceeded irrespective of which Player is being played back.
By using this feature, you can:
Categories are global settings and the corresponding information is therefore stored in the ACF file when generating the binary files for the game.
Cues are assigned to the Categories created in the global settings. Since the information about the Cue is stored in the ACB file, the ACB depends on the information contained in the ACF when using Categories. Therefore, if you edited the Categories, be sure to generate both ACF and ACB files.
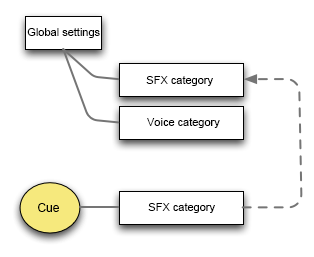
A Cue can belong to multiple Categories, for example sound effect and character voice.
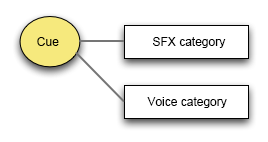
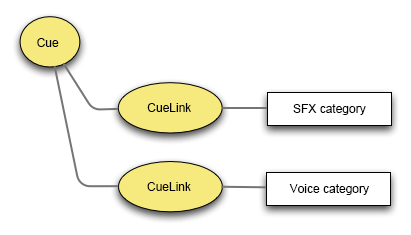
In the case of hierarchical Cues using a CueLink, each Cue is affected by the Category it belongs too, but if the linked Cue does not belong to any Category, it is affected by the Category of the referencing Cue.
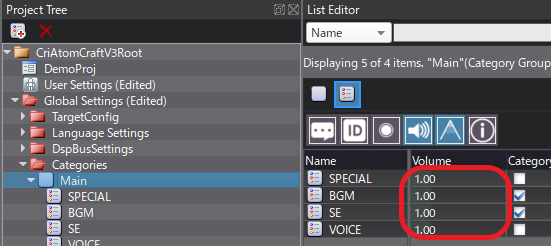
Changing a Category's volume affects the volume of all the Cues belonging to that Category.
It is able to limit the number of cue playbacks by category.
It is able to limit the multiple playback prohibition time.